By Haritha B. Veeramachaneni, MD
Patients with De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, commonly known as De Quervain’s Tendinosis, have painful tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. In De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, the first dorsal compartments are held within a tunnel-like tendon sheath. Excessive movement of the tendons causes inflammation, pain and swelling within the tendon sheath. This can be due to a thickening of the soft tissues that make up the tunnel or an increase in the amount of soft tissue within the tunnel.
Symptoms of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Patients with de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis often describe a feeling of sharp or dull pain and swelling. Pain typically occurs at the base of the thumb or at the wrist, especially with forceful gripping or twisting.
Diagnosing De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
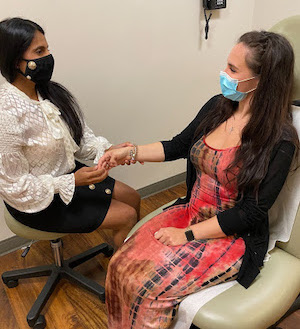
Your doctor may palpate for first dorsal compartment tenderness during the physical exam as part of the evaluation for wrist tendonitis.
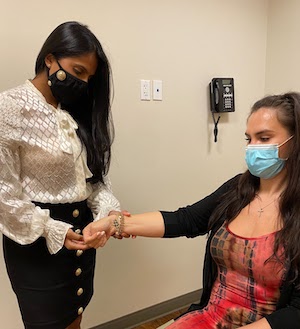
One examination maneuver your doctor may perform is the Finkelstein test which evaluates an active movement which places specific stress on the first dorsal compartment tendons to determine their degree of inflammation.
What Causes De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
The exact cause of the De Quervain’s Tendonitis is unknown, but many experts believe that changes in the use of the hand may be a cause. Repetitive movements, changes in hormones, and swelling or inflammation may also be factors.
How is De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Treated?
There are several first-line conservative treatments that may relieve symptoms:
- A splint that stops you from moving your thumb and wrist
- Tylenol or anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., Ibuprofen)
- A steroid injection into the tendon sheath
If these treatments do not help, surgery may be needed to relieve symptoms.
Contact The Institute for Hand Surgery at Long Island Plastic Surgical Group
If you suffer with wrist or thumb pain, we can help. Contact us with any questions or to schedule a consultation appointment.
Previous Post Next Post

